Booming real estate market, Hawraa Baghdad makes is even more affordable
- Industry
- Real Estate
- Location
- Baghdad
- Goals
- Every Iraqi family deserves a home
- Type
- B2C, B2B
It is part of the real estate development to track every bit of the work, from CRM to Project management on site, we built an end to end solution for Hawraa Baghdad to scale their business up
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software designed for real estate companies that integrates with an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system can provide a comprehensive solution for managing customer interactions, contracts, and payments. The CRM component can track leads, manage customer data, automate marketing processes, and provide a centralized platform for customer communication.
The ERP integration can handle accounting, contract management, installment tracking, and payment processing, streamlining financial processes and providing real-time visibility into the financial health of the business. By combining these two systems, real estate companies can improve their customer experience, increase operational efficiency, and make better-informed business decisions.
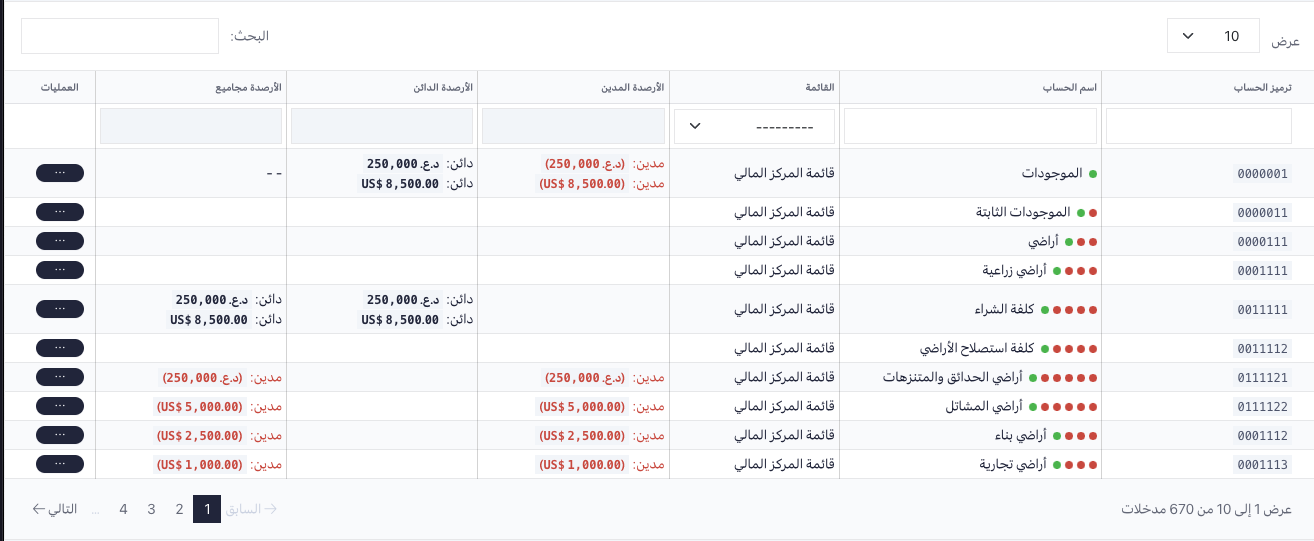
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
Accounting processes refer to the financial management and reporting functions within an ERP system. These processes typically include:
-
General Ledger: A central repository of financial information, including a record of all transactions, accounts, and balances with multiple currencies.
-
Accounts Payable: The process of managing and paying vendor invoices and expenses.
-
Accounts Receivable: The process of tracking and managing customer payments, including invoicing, receipt tracking, and collections.
-
Purchasing: The process of managing the procurement of goods and services, including purchase order creation and management, vendor selection, and inventory control.
-
Fixed Asset Management: The process of tracking and managing fixed assets, including depreciation, asset disposals, and insurance coverage.
-
Cash Management: The process of managing cash inflows and outflows, including bank reconciliation, cash forecasting, and investment management.
-
Financial Reporting: The process of generating financial reports, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
By automating these processes, an ERP system can improve accuracy, reduce manual effort, and provide real-time visibility into financial information, enabling companies to make more informed business decisions.
Manufacturing processes refer to the operations and supply chain management functions within an ERP system specifically related to manufacturing. These processes typically include:
-
Materials Management: The process of managing raw materials, including inventory control, purchasing, and vendor selection.
-
Production Planning: The process of scheduling and coordinating the production of goods, including capacity planning, material requirements planning, and production scheduling.
-
Work Order Management: The process of managing and tracking work orders, including cost tracking, resource allocation, and quality control.
-
Bill of Materials: The process of managing the components required to manufacture a product, including the creation and management of bills of materials and product structures.
-
Quality Control: The process of monitoring and controlling the quality of goods, including inspection processes, corrective actions, and continuous improvement initiatives.
-
Shop Floor Control: The process of monitoring and controlling production activities on the shop floor, including real-time data collection and analysis.
-
Supply Chain Management: The process of managing relationships with suppliers, including procurement, logistics, and inventory management.
By automating these processes, an ERP system can improve production efficiency, reduce manual effort, and provide real-time visibility into production and supply chain information, enabling manufacturers to make more informed business decisions.
SCM (Supply Chain Management) processes refer to the operations and supply chain management functions within an ERP system. These processes typically include:
-
Procurement: The process of purchasing goods and services, including the creation and management of purchase orders, vendor selection, and supplier management.
-
Inventory Management: The process of managing the flow of goods, including inventory control, replenishment planning, and stock management.
-
Warehouse Management: The process of managing the storage and movement of goods in a warehouse, including receiving, shipping, and stock control.
-
Logistics: The process of managing the movement of goods, including transportation, delivery, and shipping management.
-
Demand Planning: The process of forecasting demand for goods, including statistical forecasting, collaborative forecasting, and demand planning.
-
Supplier Relationship Management: The process of managing relationships with suppliers, including supplier performance management, supplier development, and supplier collaboration.
-
Quality Control: The process of monitoring and controlling the quality of goods, including inspection processes, corrective actions, and continuous improvement initiatives.
By automating these processes, an ERP system can improve supply chain efficiency, reduce manual effort, and provide real-time visibility into supply chain information, enabling organizations to make more informed business decisions.
HCM (Human Capital Management) processes refer to the human resources and payroll functions within an ERP system. These processes typically include:
-
Employee Management: The process of managing employee data, including personal information, job information, and payroll information.
-
Recruitment and Onboarding: The process of attracting, hiring, and integrating new employees, including applicant tracking, job postings, and new-hire orientation.
-
Performance Management: The process of managing employee performance, including performance evaluations, goal setting, and development planning.
-
Time and Attendance: The process of tracking and managing employee time and attendance, including time sheets, leave requests, and absence tracking.
-
Payroll and Compensation: The process of managing employee compensation, including payroll processing, tax calculation, and benefits administration.
-
Learning and Development: The process of managing employee learning and development, including training programs, e-learning, and certification tracking.
-
Succession Planning: The process of identifying and developing future leaders, including talent management, career development, and leadership programs.
By automating these processes, an ERP system can improve HR efficiency, reduce manual effort, and provide real-time visibility into HR information, enabling organizations to make more informed business decisions.
“ I just wanted to say that I'm very happy with working with TwoAbstracts. The level of competency and support are unmatched. ”
Related stories

An ERP system is designed for high volume distribution, logistics, and accounting, making it a comprehensive solution for managing all …

A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software designed for real estate companies that integrates with an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system …

Our medical educational mobile application is designed to revolutionize the way healthcare professionals access and engage with medical education. With …